CONTENTS
№ 1 (14),
2005
I.
NUCLEAR PHYSICS
|
|
|
1.
Shells, orbits and transport coefficients of the nuclear collective
dynamics
A. G. Magner, A. N.
Gzhebinsky, S. N. Fedotkin............................................................... |
|
2. About
the Coulomb and nuclear dissociation of deuterons in the field of
atomic nuclei
M.
V. Evlanov, A. M. Sokolov, V. K. Tartakovsky, K. O. Terenetsky................................. |
|
3. New potential of the
one-particle model of alpha-decay
V. V. Davydovskyy, A. K. Zaichenko, V. S.
Olkhovsky.......................................................
|
|
4.
Coincidence cross-section of process 3He(e, e˘p)2H
calculation using the diffraction
nuclear model
V. K. Tartakovsky, A.
V. Fursayev, A. D. Voytsekhovskaya............................................... |
|
5.
Occupation of
levels for
nγ-reaction and middle square projection of the single-particle
momentum of
nucleons
Yu. G. Schepkin, V. I. Slisenko, Т. А. Kostyuk.................................................................... |
|
6. 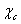 production
in pA collisions at HERA-B experiment production
in pA collisions at HERA-B experiment
Yu. V. Pylypchenko.............................................................................................................
|
|
|
|
II. NUCLEAR POWER |
|
|
|
I. M. Vyshnevskyi................................................................................................................ |
|
8.
Assessment of WWER-type
reactor vessels radiation lifetime of Ukrainian
NPPs
E. U. Grynik, L. I.
Chyrko, V. M. Revka............................................................................
|
|
|
III.
RADIATION PHYSICS
|
|
|
9.
Charge accumulation and electric fields in lava-like fuel containing
materials
O. S. Zinets.........................................................................................................................
|
|
|
|
IV. RADIOECOLOGY AND
RADIOBIOLOGY |
|
|
|
10. A model of 137Cs
root uptake at the initial stage of ontogenesis of some cultivated
plants
A. N. Berlizov, D. M. Grodzynsky,
N. M. Rashydov,
V. V. Tryshyn, V. V. Berezhna............................................................................................ |
|
11. Formation of
cytogenetic anomales at the condition of prolonged exposure with low
dose rate
A. P. Kravets, G. D.
Slinyavchuk, T. A. Vasilenko.............................................................. |
|
12.
Investigation of ratio “strontium - calcium” in the plants and in
the corresponding soil solution for 90Sr and for
natural total strontium
V. V. Prorok, C. F. V. Mason, A. P. Ganushevich,
V. V. Ostashko,
T. I.
Makarenko, L.
Yu.
Melnichenko....................................................... |
|
13. Analysis of the Chornobyl
zone’s forests state based on the red edge position with use of
the multispectral SPOT-4
images and ground-based reflectance and fluorescence spectra
research
V. I. Lyalko, A. I.
Sakhatsky, Z. М. Shportiuk, A. Ya. Khodorovsky, A. T. Azimov,
|
|
14. Optimization of uncertainty measurement of
radionuclides activity during the performance of radoiecological
inspections
Yu. V. Khomutinin.............................................................................................................. |
|
15. Dynamics of distribution of 137Cs in
external and internal organs and tissues of
fishes of different ecological groups of cooling-pond of Chornobyl
NPP
O. L. Zarubin..................................................................................................................... |
|
16.
Response reactions of the fungi, isolated from inner
locations of “Ukryttya”,
which have different
levels of radioactivity
T. I. Tugay, N. M. Zhdanova, V. O. Zheltonozhsky,
L. V. Sadovnikov, M. V. Telichko.......................................................................................
|
|
17. Development of
ion exchange determination
methodology of uranium and transuranium
elements in ground waters and liquid radioactive waster of
“Ukryttya” object
А. А. Odintsov, D.
V. Bogutskiy......................................................................................... |
|
18.
Application of gamma spectrometric logging for identification of
sources of
radioactive
contamination of underground medium
M. I. Panasyuk, A. D.
Skorbun, M. I. Pavlyuchenko......................................................... |
|
19.
Development of method structure determination of soil contamination
by 137Cs
of object “Ukryttya” site under the results of
gamma-spectrometric investigations
А. К. Kalynovsky, V. G.
Batiy, А. А. Pravdyvyi................................................................. |
|
|
|
V. ENGINEERING AND METHODS OF EXPERIMENT |
|
|
|
20.
Utilization of the magnet monohromator of the isohron cyclotron
U-240 for
the stable ions
separation
O. E. Valkov, O. V. Demiynov, O. V. Dolinski,
M. E. Dolinska, Yu. I. Kamyshnikov..................................................................................
|
|
21.
Acceleration of 14N ions on U-120 cyclotron. First
results
S. V. Adamenko, A.
E. Borzakovsky, O. Yu. Goryunov, V. I. Kuts,
V. A. Ryloshko, N.
G. Tolmachov, A. A. Shvedov.............................................................. |
1. SHELLS,
ORBITS AND TRANSPORT COEFFICIENTS
OF THE NUCLEAR COLLECTIVE
DYNAMICS
A. G. Magner, A. N. Gzhebinsky,
S. N. Fedotkin
The Strutinsky shell
correction method is applied to the nuclear collective dynamics within the
periodic orbit theory extended to dissipative phenomena through some effective
residue interactions. The macroscopic limit of the semiclassical transport
coefficients with the known
wall formula for the friction is obtained. The shell corrections to the
stiffness, the inertia and the friction parameters are calculated analytically
as function of the particle number and temperature for the low-energy
excitations of heavy nuclei. It is shown that they are approximately
proportional to the free-energy shell corrections, with the same sign for the
inertia and the opposite one for the stiffness and the friction. The shell
oscillating components of the transport coefficients disappear exponentially at
temperatures larger than the ones of the free energy. The reduced friction and
the energy excitation estimations are in agreement with some experimental data
and theoretical calculations.
2.
ABOUT
THE COULOMB AND NUCLEAR
DISSOCIATION OF DEUTERONS
IN THE FIELD OF ATOMIC NUCLEI
M. V. Evlanov,
A. M. Sokolov, V.
K. Tartakovsky, K. O. Terenetsky
The calculation of differential
cross sections of the Coulomb dissociation of deuterons is performed, when the
nucleons emit under zero angles. Comparison between the calculated cross section
of deuteron diffraction dissociaton with allowance of the Coulomb interaction
and corresponding experiments is made. The deuteron dissociation experiments in
the field of nuclei under zero angles of nucleon emission are satisfactorily
described taking into account the Coulomb and nuclear interactions.
3. NEW POTENTIAL
OF THE ONE-PARTICLE
MODEL OF ALPHA-DECAY
V.
V.
Davydovskyy,
A.
K.
Zaichenko,
V.
S.
Olkhovsky
Phenomenological one-particle
model of alpha-decay,
which is based on a
mechanism of alpha-particle
tunneling through Coulomb barrier, is proposed. In contrast to classical models
of Gamow and Landau, calculations of the barrier penetrability are carried out
with no use of quasiclassical approximation as well as the processes of
formation and disappearance of alpha-particles in the surface layer of parent
nucleus are taken into account. In the framework of this model, explicit
relations for the Coulomb barrier penetrability, the phase tunneling and
reflection time of alpha-particles as well as for the alpha-particle formation
time are obtained. In addition, the
program for development of time microscopic theory of alpha-decay
of non-spherical nuclei, which is aimed not only to describe existing
experimental data on alpha-decay of deformed nuclei, but also to plan new
experiments, is given.
4. calculation
OF Coincidence cross-section of 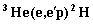 process
process
using
the diffraction nuclear model
V. K.
Tartakovsky, A. V. Fursayev, A. D. Voytsekhovskaya
The cross-section of 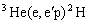 process
is calculated with the regard to the interaction in the final state in terms of
diffraction nuclear model. The satisfactory agreement with coincidence
experiment is obtained without using any adjusting parameters. The influence of
nuclear structure and interaction as well as kinematics changes on the
cross-section behaviour is investigated.
process
is calculated with the regard to the interaction in the final state in terms of
diffraction nuclear model. The satisfactory agreement with coincidence
experiment is obtained without using any adjusting parameters. The influence of
nuclear structure and interaction as well as kinematics changes on the
cross-section behaviour is investigated.
5.
OCCUPATION
OF
LEVELS
FOR
nγ-REACTION
AND
MIDDLE
SQUARE
PROJECTION
OF
THE
SINGLE-PARTICLE
MOMENTUM
OF
NUCLEONS
Yu. G. Schepkin,
V.
I. Slisenko, Т.
А. Kostyuk
The calculation of the
relation between the nuclear levels occupation
by means of gamma-rays emission and projection middle square
<m2> of the single-partical
momentum of nucleons were performed. It is shown that
the increasing of spin difference berween ground occupated levels is caused by
the decreasing of statistical model parameters uncertaintly which is determined
from the value of occupation numbers. Ground state and compaund nucleus level
densities and correction on even-odd difference of binding energies of nucleus
and single-particle strength functions as parameters for culculations have been
choosen.
6.
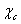 PRODUCTION
IN pA
COLLISIONS AT HERA-B
EXPERIMENT
PRODUCTION
IN pA
COLLISIONS AT HERA-B
EXPERIMENT
Yu.
V. Pylypchenko
We report on the measurement of fraction of
J/Y
produced via radiative decays of 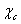 mesons,
mesons,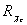 ,
in collisions of 920 GeV protons with carbon nuclei. Analyzed
data were collected by HERA-B detector in 2002 using di-muon trigger. The
preliminary value is
,
in collisions of 920 GeV protons with carbon nuclei. Analyzed
data were collected by HERA-B detector in 2002 using di-muon trigger. The
preliminary value is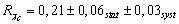 ,
for the events with
,
for the events with 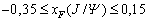 .
.
7. ROLE OF NUCLEAR POWER IN UKRAINE
I. M. Vyshnevskyi
Nuclear power of Ukraine commenced from Chornobyl
NPP, where the first unit was put into operation at 1977. At present in Ukraine
there are 4 running NPPs with a total installed capacity 11880 MW where more
than 40 % of electricity is generated. Elaborated Atomic Energy Strategy
Development for the period till 2030 after the commissioning of two new units in
2004 foresees to keep the total installed capacity around 14000 MW. Analysis on
the maintenance of such level and the solution of other problems, related to
nuclear energy is carried out. Among them: nuclear fuel cycle, handling of
radioactive wastes, decommissioning and others. Thus nuclear energy plays and
will play the important role to ensure the electricity generation in Ukraine.
8. Assessment of WWER-type reactor vessels radiation
lifetime
of
Ukrainian NPPs
E. U. Grynik, L. I. Chyrko, V.
M. Revka
The Ni content in the welds of 9 energetic units
of WWER-1000 type NPPs operating in Ukraine now exceeds the standard value. The
increase of the Nickel concentration beyond the regulated one is known to lead
to the increase of the irradiation embrittlement rate. The highest content of
Nickel is in the weld metal of Khmelnitsky NPP-1 and it is equal to 1,88 %.
Therefore, the paper considers just this case as the most complicated.
In the paper the performed analysis
of the dependence of the brittle critical temperature of the weld metal on the
accumulated neutron fluence has shown the critical temperature not to exceed
(with the confidence probability 95%) the regulated dependence. Thus, the state
of the weld metal does not limit the design lifetime of the given reactor
vessel.
9. CHARGE
ACCUMULATION
AND
ELECTRIC
FIELDS
IN
LAVA-LIKE
FUEL
CONTAINING MATERIALS
O. S. Zinets
The charge accumulation and electric fields due
to internal radioactivity in lava-like fuel containing materials has been
considered. It has been shown that macroscopic electric fields can be as large
as 104 V/cm at the material surface and at the interface of a
spherical inclusion - SiO2 matrix for the total activity
1 GBk × сm-3.
The mechanical stresses connected with such fields are small (102 Pa)
and have a small influence on the material destruction.
10.
A MODEL OF 137Cs
ROOT UPTAKE AT THE INITIAL STAGE OF ONTOGENESIS OF SOME CULTIVATED
PLANTS
A. N. Berlizov, D. M. Grodzynsky,
N. M. Rashydov,
V. V. Tryshyn,
V. V. Berezhna
On the basis of the data, obtained in the
laboratory experiments, a phenomenological two-parameter model was developed for
137Cs root uptake at the initial stage of ontogenesis of some
cultivated plants - wheat, rye, maize, pea, bean, and soybean. Within the
framework of the common approach the model describes the radionuclide
accumulation by the plants with different types of the root system grown on soil
with significantly different character of radionuclide contamination vertical
profiles of the soil. The model parameters have adequate interpretation. The
parameter values, defined as a result of the experimental data fitting, allow
predicting values of the uptake coefficients for the investigated cultivated
plants for an arbitrary vertical profile of radioactive contamination. Besides,
the model provides the information about peculiarities of the mineral substance
uptake by plants at the initial stage of their ontogenesis.
11. FORMATION
OF
CYTOGENETIC
ANOMALES
AT
THE
CONDITION OF
PROLONGED
EXPOSURE WITH
LOW
DOSE
RATE
A. P. Kravets, G. D. Slinyavchuk,
T. A. Vasilenko
The properties of chromosomal aberration
formation on condition of prolonged exposure had been investigated. It is
demonstrated that risk of cytogenetic anomalies on condition of prolonged
exposure may be in 1 - 2 order higher then one for the condition of acute
exposure. Possible consequences of prolonged exposure for realization of cancer
and genetic risks had been discussed.
12. INVESTIGATION
OF
RATIO
“STRONTIUM
-
CALCIUM”
IN
THE PLANTS
AND
IN
THE CORRESPONDING
SOIL
SOLUTION
FOR
90Sr
AND
FOR
NATURAL
TOTAL
STRONTIUM
V. V. Prorok,
C.
F. V. Mason, A.
P. Ganushevich, V.
V. Ostashko,
T. I. Makarenko,
L.
Yu. Melnichenko
Ratios Sr/Ca for natural total strontium and
90Sr/Ca in the plants and in the corresponding soil solutions for three
experimental lands with “fuel” type of pollution for several plants at natural
conditions are determined. The lands with tree different types of soil are at
the Exclusive Zone of the Chernobyl Power Station. The obtained experimental
results shown that ratio Sr/Ca in plant is equal to this ratio in the
corresponding soil solution for all investigated lands and plants. Ratio 90Sr/Ca
in plant exceeds this ratio at the corresponding soil solution.
13. Analysis
of
THE
ChOrnobyl
zone’s
forests
state
BASED
on
THE
Red
Edge
Position
WITH
USE
OF
THE
multispectral
SPOT-4
imageS
and
ground-based
reflectance
and
fluorescence
spectra
research
V. I. Lyalko,
A.
I. Sakhatsky, Z.
М. Shportiuk, A.
Ya. Khodorovsky, A.
T. Azimov,
O. M. Sybirtseva,
O.
I. Levchik, O.
V. Svarichevska, L.
V. Skripka
The results of the ground-based research of visible
reflectance and laser-induced fluorescence of pine (needles) at different stages
of pine fungus damage, depending on crown position and content of incorporated
radionuclides 137Cs and 90Sr, as well as the results of
the remote sensing data of the Red Edge Position of pine forests growing in
Chernobyl zone with use of multispectral SPOT-4 images are presented. It has
been established that the remote sensing data, which take into account integral
state of the tested territory is more effective for the detection of root sponge
stress.
14.
OPTIMIZATION
OF
UNCERTAINTY
MEASUREMENT
OF
RADIONUCLIDES
ACTIVITY DURING
THE
PERFORMANCE
OF
RADOIECOLOGICAL
INSPECTIONS
Yu.
V.
Khomutinin
Some issues of optimization of uncertainty
measurement during the performance of radioecological inspections are
considered. The criterion of definition by maximum permitted uncertainty of
radionuclide activity measurement and the methods of its calculation are
proposed. It is shown that at estimation of median individual test of ground
activity the density of site pollution specific activity of crop on site etc.
with the set accuracy and reliability should not aspire to high accuracy of
individual activity measurement in the sample. It is more preferable to select
some additional tests or samples and activity measurement to be performed with
more statistical uncertainty.
15. DYNAMICS OF DISTRIBUTION OF 137Cs IN
EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL ORGANS AND TISSUES OF FISHES OF DIFFERENT
ECOLOGICAL GROUPS OF COOLING-POND OF CHORNOBYL NPP
O. L. Zarubin
Dynamics of the
137Cs contents in different organs and tissues of fishes of the
cooling-pond of ChNPP is studied from 1986 to 1990.
The measurements
were performed
by gamma-spectrometer
methods. The contents of
137Cs in the organism of the majority of species of fishes has
achieved the maximal values during 1 - 4 months from the moment of the accident.
Relatively even contamination of 137Cs in all organisms of fishes was
registered at this time. Differentiation in accumulation of 137Cs by
different organs and tissues with the course of time is increased, and in
tissues, directly contacting with water, the contents of 137Cs was
decreased more strongly. The specific features of 137Cs distribution
on organs and tissues are found.
16. Response reactions OF THE FungI, isolated
from inner locations of “UKRYTTYA”, which have differENT levels of
radioactivity
T. I. Tugay, N. M. Zhdanova, V. O. Zheltonozhsky, L. V. Sadovnikov, M. V.
Telichko
Adaptive reactions of some
fungi strains of species Cladosporium chlorocephalum and Aspergillus versicolor,
which was isolated from inner location of Shelter with different level of
radioactive pollution, in relation to the action of two sources of ionizing
irradiation 121Sn and 137Cs have been studied. Correlation
between radiotropic reaction and radioactive pollution level inner locations was
shown. Is established that under exposure of radiation enhanced of conidia
germination only at strains is observed, isolated from inner locations with a
rather low level radioactivity. Under action 137Cs was observed
inhibition of process of conidia germination and emergent hyphae length at dark
pigmented strains and activation of these processes at light pigmented strains.
The degree of these effects did not depend on the level of radioactivity of
places, where the strains were isolated.
17. DEVELOPMENT
OF
ION
EXCHANGE
DETERMINATION
METHODOLOGY
OF URANIUM
AND
TRANSURANIUM
ELEMENTS
IN
GROUND
WATERS
AND LIQUID
RADIOACTIVE
WASTER
OF
“UKRYTTYA”
OBJECT
А. А.
Odintsov, D. V. Bogutskiy
The procedure of
simultaneous determination of the contents of radionuclides 234-238U,
238Pu, 239+240Pu, 241Am and 244Cm in
ground water and liquid radioactive waster is submitted ion exchange.
Concentration and separations of uranium and plutonium is yielded on anion AV-17
in Cl - form. The clearing of americium and curium from rare earth elements is
carried out step-by-step striping from a cation-exchange column with KU - 2-8.
Activity of isotopes of uranium, plutonium, americium and curium determine by
alpha spectrometric measurements.
18. APPLICATION
OF GAMMA SPECTROMETRIC LOGGING FOR IDENTIFICATION OF SOURCES OF
RADIOACTIVE CONTAMINATION OF UNDERGROUND MEDIUM
M. I. Panasyuk, A. D. Skorbun, M. I.
Pavlyuchenko
Using the results of the joint analysis of the
bulk and spectrometric gamma logging, that have been carried out in boreholes
around power Unit 4 of Chornobyl nuclear power plant, the regions of
radioactive contamination of soils below the pre-accident level of the ground
have been discovered. It was shown, that gamma-logging data in combination with
hydrogeology data gives the possibility to distinguish the influence of
potential sources of radionuclides. For instance, soils, contaminated by fuel
particles, high active water from Unit 4, etc.
19. DEVELOPMENT OF METHOD STRUCTURE DETERMINATION OF
SOIL CONTAMINATION BY 137Cs
OF OBJECT “Ukryttya” SITE UNDER
THE
RESULTS OF GAMMA-SPECTROMETRIC INVESTIGATIONS
А.
К.
Kalynovsky, V. G. Batiy, А.
А.
Pravdyvyi
Structure analysis method of soil contamination by 137Cs
under the results of spectrometric investigations of gamma-radiation in
boreholes passing through radioactively contaminated soils was developed. For
practical implementation, the field spectrometric complex was created and
required methodical measurements were performed at experimental models as on
study of gamma-radiation characteristics. Mathematical model of borehole was
proposed adequate to experimental models for calculations using MCNP4 software
code. The results of practical application during radioactive contamination
structure analysis of soils making geological section of local zone of Object
“Ukryttya” were stated.
20. UTILIZATION
OF
THE
MAGNET
MONOHROMATOR
OF
THE
ISOHRON
CYCLOTRON
U-240
FOR THE
STABLE
IONS
SEPARATION
O.
E. Valkov,
O.
V. Demiynov,
O.
V. Dolinski,
M.
E. Dolinska,
Yu.
I. Kamyshnikov
This paper reviews one of
the possible variant of the electromagnetic separator for stable isotopes
production with analyzing magnet inhomogeneous magnetic field. Detailed beam
optical calculations are described for chosen ion-optical scheme of the
separator. Results shows that this magnet can be used for isotopes production
with excellent efficiency for any ion mass. Factors affecting the separation
process – beam parameters, space-charge and aberrations are discussed.
21. ACCELERATION
OF
14N
IONS
ON
U-120
CYCLOTRON. FIRST
RESULTS
S. V. Adamenko,
A.
E. Borzakovsky,
O. Yu. Goryunov,
V. I. Kuts,
V. A. Ryloshko,
N.
G. Tolmachov, A.
A. Shvedov
The new spectrometric
regime - intensive beam of 14N++ with 8,7 MeV energy was
obtained on the classic U-120 cyclotron. Back-scattering spectra on different
samples with heavy elements on a surface of a light matrix were obtained with
the help of time-of-flight method. The feasibility of such beam use for
indication of microquantities of heavy elements (1011 atoms /cm2),
located on a surface of a light matrix is shown.